ubuntu自定义一个service制作开机自启脚本,nacos开机自启
本文共 1509 字,大约阅读时间需要 5 分钟。
Ubuntu没有自带其他linux版本自带的rc.local文件的开机自启动方法,所以要自己生成rc.local文件,其实就是自定义一个service服务
就像大家平时使用的service
service xxx start # 尝试手动启动服务,看是否能正常运行service xxx status # 查看服务运行状态service xxx stop # 手动停止服务
第一步:编写service服务
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/myselfTest.service # 编写service服务
myselfTest:文件名,可随意设置。
myselfTest.service文件内容这里我以设置nacos服务开机自启为例
[Unit]# 描述,随你怎么写Description=Cclient desktop virtualization serviceAfter=network.target# 这里是关键[Service]# 后台运行模式,服务类型,具体可以自行百度,设置成自己想要的Type=forking# 所属用户#User=szyd# 所属组#Group=szyd# 重启#Restart=alwaysTimeoutSec=0# 配置重新启动服务之前的睡眠时间,重启频率,比如某次异常后,等待5(s)再进行启动,默认值0.1(s)#RestartSec=60# 这是服务运行的具体执行命令,可执行执行脚本的绝对路径,即对应的service start/stop/reloadExecStart=/home/ubuntu/installer/nacos/bin/startup.sh -m standaloneExecReload=/home/ubuntu/installer/nacos/bin/shutdown.shExecStop=/home/ubuntu/installer/nacos/bin/shutdown.sh[Install]# 这里你没太大要求可以不管WantedBy=multi-user.target
Type=forking,我这里的理解是通过ExecStart启动脚本后成功了,本身的myselfTest这个服务还会一直挂在后台,通过service myselfTest status可以看到active状态,而Type=simple则在ExecStart启动成功之后,就直接推出了,所以看myselfTest服务会是inactive状态.
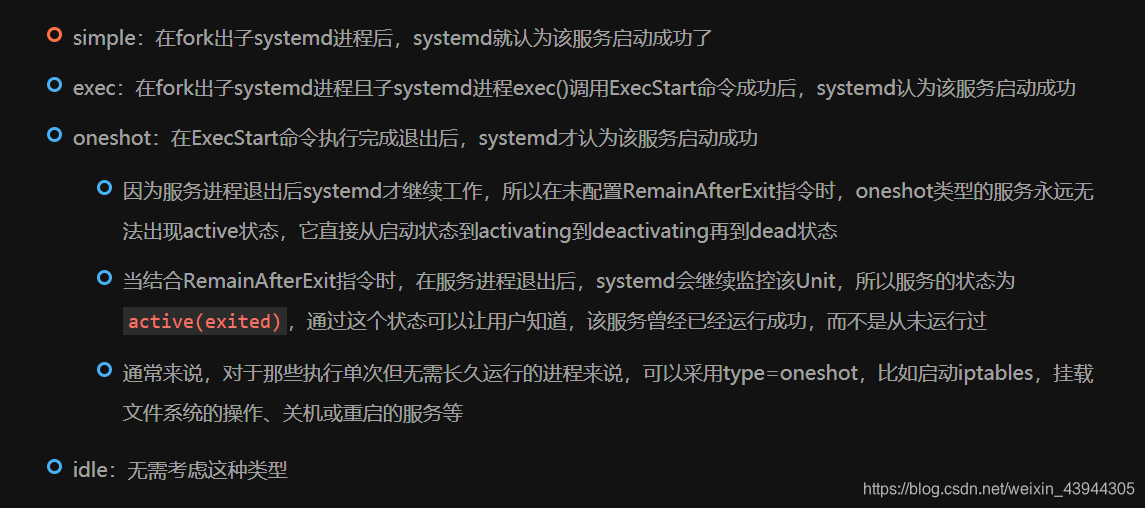
关于Type=forking想进一步了解的话,可以看一下大佬的博客
第二步:编写shell脚本
下面是个假脚本,就是上面service中要执行的脚本,大家自己写就行了

nacos的话这里还要注意一点,在startup.sh脚本中要把jdk变量设置为绝对路径 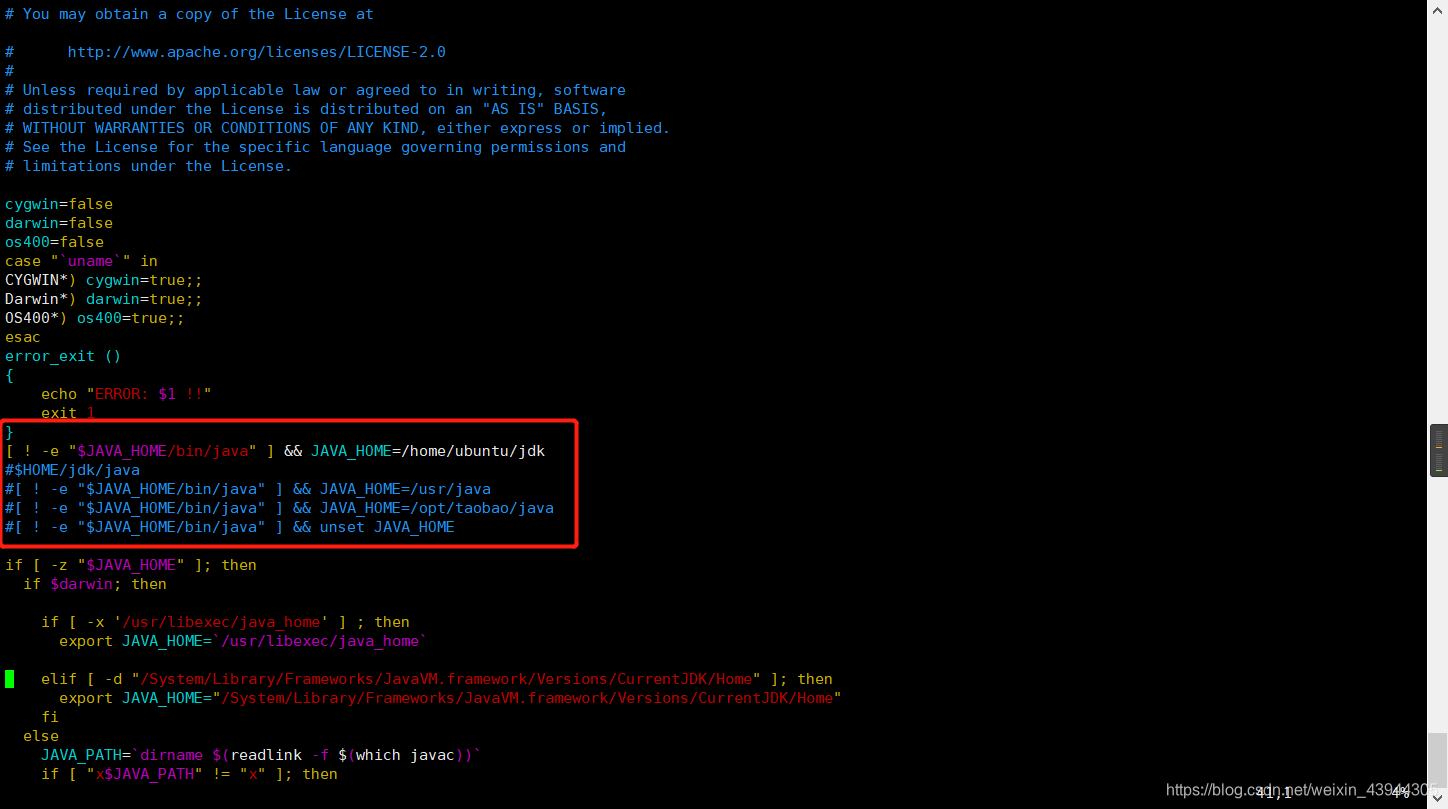
第三步:设置为自启动服务
Ubuntu18.04版本之后,就采用了systemctl来控制开机自启动服务
sudo systemctl daemon-reload #重新加载service服务sudo systemctl enable myselfTest.service # 启用服务sudo systemctl is-enabled myselfTest.service # 查看启用状态service myselfTest start # 尝试手动启动服务,看是否能正常运行service myselfTest status # 查看服务运行状态service myselfTest stop # 手动停止服务
启动成功
转载地址:http://fwvpz.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章